
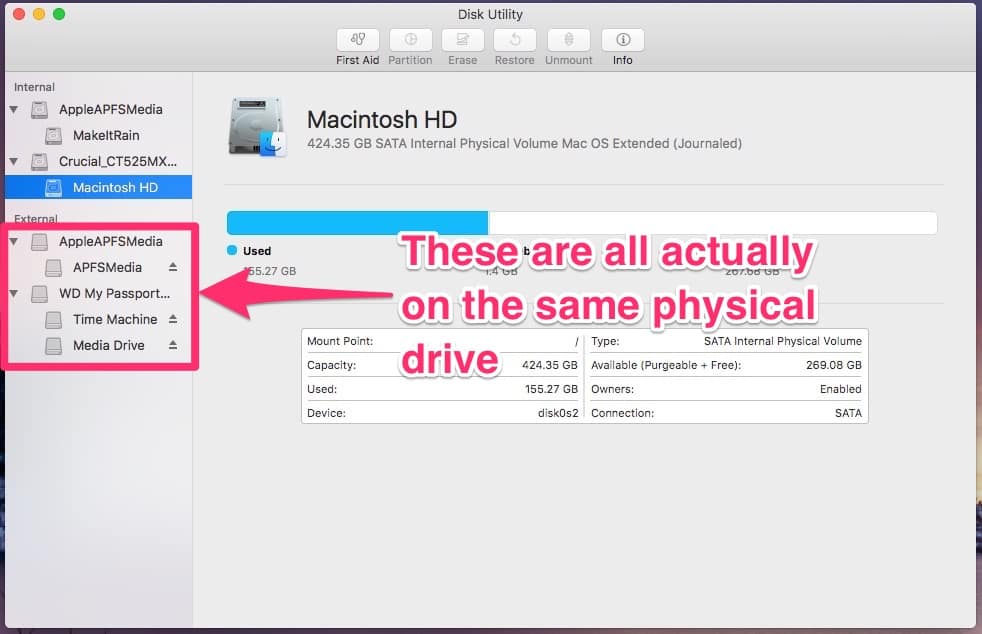
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ElCapDiskUtilityRestore-5727c7573df78ced1f043999.jpg)
For example, RawWrite and WinImage create floppy disk image files for MS-DOS and Microsoft Windows. The software required varies according to the type of disk image that needs to be created. Typically, disk imaging requires a third party disk imaging program or backup software.
Disk images became much more popular when floppy disk media became popular, where replication or storage of an exact structure was necessary and efficient, especially in the case of copy protected floppy disks.ĭisk image creation is called disk imaging and is often time consuming, even with a fast computer, because the entire disk must be copied. The early ones were as small as 5 megabytes and as large as 330 megabytes, and the copy medium was magnetic tape, which ran as large as 200 megabytes per reel. Background ĭisk images were originally (in the late 1960s) used for backup and disk cloning of mainframe disk media. Despite the benefits of disk imaging the storage costs can be high, management can be difficult and they can be time consuming to create. Proprietary formats are typically used by disk imaging software. Virtual disk images (such as VHD and VMDK) are intended to be used for cloud computing, ISO images are intended to emulate optical media and RAW disk images are used for forensic purposes. Disk images can be made in a variety of formats depending on the purpose. Disk imaging is done for a variety of purposes including digital forensics, cloud computing, system administration, as part of a backup strategy, and legacy emulation as part of a digital preservation strategy. Compression and deduplication are commonly used to reduce the size of the image file set. Traditionally, disk images were bit-by-bit copies of every sector on a hard disk often created for digital forensic purposes, but it is now common to only copy allocated data to reduce storage space. For ISO 9660 image files, see ISO image.Ī disk image is a snapshot of a storage device's structure and data typically stored in one or more computer files on another storage device.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
